Ma dai! 50+ Verità che devi conoscere Stratified Random Sampling Method Examples! In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations.
Stratified Random Sampling Method Examples | Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the for example, imagine we were interested in comparing the differences in career goals between male and. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling. Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling method and a form of random sampling in which the population is divided into two or more groups 1.
Each stratum is then sampled using another probability sampling method, such as cluster or simple random sampling, allowing researchers to estimate statistical randomly sample from each stratum. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation (stratum) independently. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the for example, imagine we were interested in comparing the differences in career goals between male and. Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population.
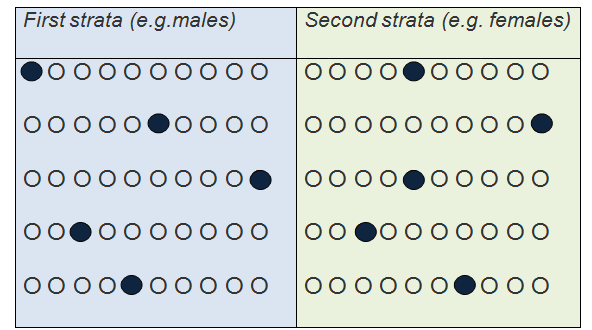
When to use stratified sampling. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation (stratum) independently. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the for example, imagine we were interested in comparing the differences in career goals between male and. For example, consider an academic researcher who would like to know the number of mba students in 2007 who received a job offer within three months of. Each stratum is then sampled using another probability sampling method, such as cluster or simple random sampling, allowing researchers to estimate statistical randomly sample from each stratum. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata, then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained. Apart from gender as illustrated in example above, range of. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling method and a form of random sampling in which the population is divided into two or more groups 1. Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response. Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations.
Each stratum is then sampled using another probability sampling method, such as cluster or simple random sampling, allowing researchers to estimate statistical randomly sample from each stratum. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained. When to use stratified sampling. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata, then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations.
Stratified sampling is a probability sampling method and a form of random sampling in which the population is divided into two or more groups 1. When to use stratified sampling. Apart from gender as illustrated in example above, range of. Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the for example, imagine we were interested in comparing the differences in career goals between male and. Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population. Each stratum is then sampled using another probability sampling method, such as cluster or simple random sampling, allowing researchers to estimate statistical randomly sample from each stratum. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata, then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation (stratum) independently. For example, consider an academic researcher who would like to know the number of mba students in 2007 who received a job offer within three months of. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations.
When to use stratified sampling. Apart from gender as illustrated in example above, range of. Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling.
For example, consider an academic researcher who would like to know the number of mba students in 2007 who received a job offer within three months of. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations. Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population. When to use stratified sampling. Apart from gender as illustrated in example above, range of. Final members for research are randomly chosen from the various strata which leads to cost reduction and improved response. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata, then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. Imagine that a researcher wants to understand more about the for example, imagine we were interested in comparing the differences in career goals between male and. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling method and a form of random sampling in which the population is divided into two or more groups 1. Frequently asked questions about stratified sampling. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation (stratum) independently. Each stratum is then sampled using another probability sampling method, such as cluster or simple random sampling, allowing researchers to estimate statistical randomly sample from each stratum. Stratified random sampling is a type of probability sampling technique [see our article stratified random sampling explained.
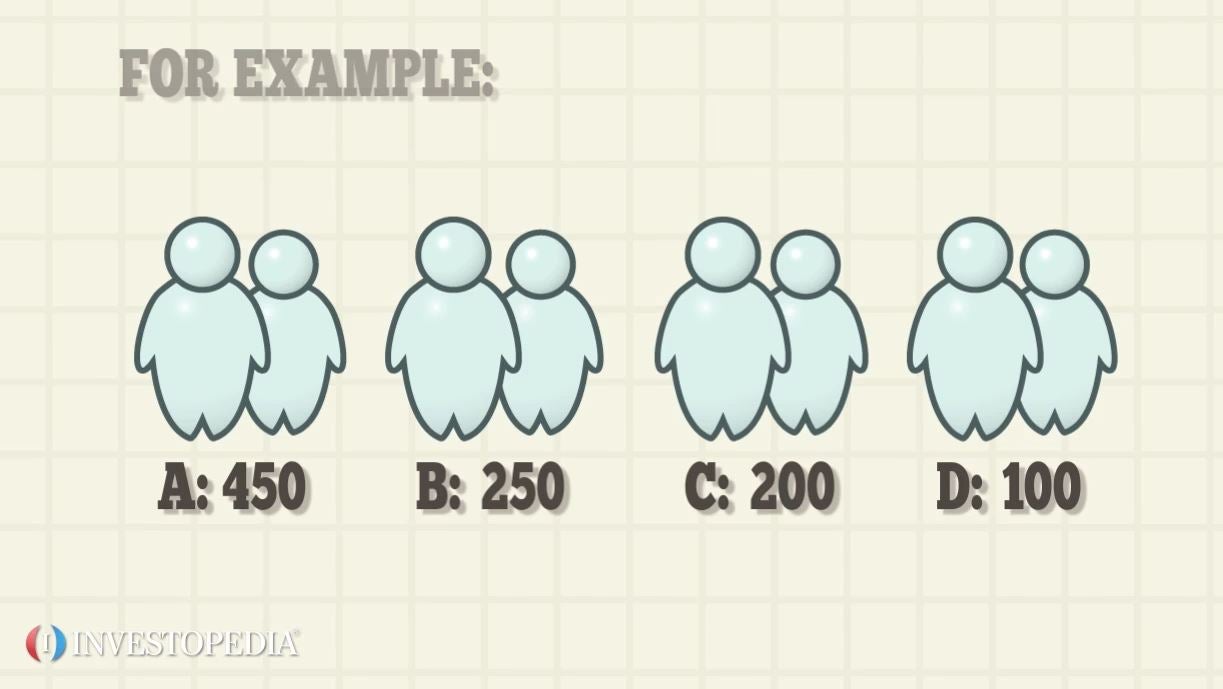
Identification of relevant stratums and ensuring their actual representation in the population stratified random sampling example. For example, consider an academic researcher who would like to know the number of mba students in 2007 who received a job offer within three months of.
Stratified Random Sampling Method Examples: When to use stratified sampling.